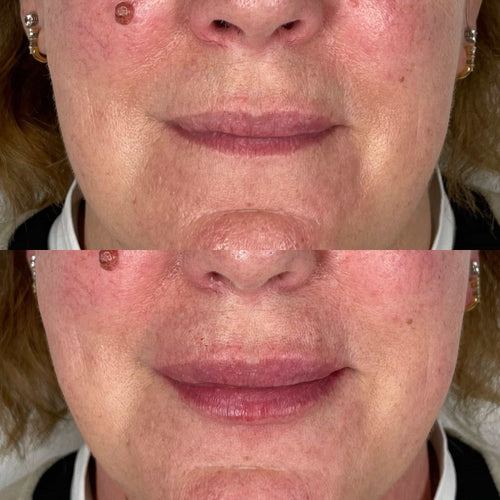
Book Your Dermal Filler Session with Dr. Laura Geige Today
Types of Fillers
1. Dental Filler Materials
Dental fillers are substances used to restore teeth that have been damaged by decay or trauma. They come in various forms, each with its own unique characteristics and purposes.
The types of dental filler materials can be broadly categorized into several groups, including: amalgam, composite resin, ceramic, gold, glass ionomer, and polymeric composites.
Amalgam fillers are the oldest type of dental filling material. They consist of a mixture of mercury, silver, tin, and copper alloys that are molded into a tooth shape. While they have been used for over 150 years, their use has declined in recent years due to concerns about mercury toxicity.
Composite resin fillers, on the other hand, are the most popular choice among dentists today. They are made up of a mixture of plastics and glass particles that are molded into a tooth shape. Composite resin fillers are tooth-colored and can be used to repair front teeth and other visible areas of the mouth.
Ceramic fillers are another type of dental material that is becoming increasingly popular. They are made from inorganic materials such as porcelain or ceramic powder, which are molded into a tooth shape using advanced technology. Ceramic fillers are known for their strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal.
Gold fillers, also known as gold inlays, are the most expensive type of dental filling material. They consist of thin layers of gold alloy that are bonded to a tooth using special cement. Gold fillers are often used for large cavities or teeth with significant structural damage.
Glass ionomer fillers are another type of dental material that has gained popularity in recent years. They are made from a mixture of glass particles and acid, which react when exposed to saliva to form a hardened matrix. Glass ionomer fillers release fluoride over time, making them beneficial for teeth with decay.
Polymeric composites are the newest type of dental filling material, having been developed in the last few decades. They consist of a mixture of plastics and other materials that are molded into a tooth shape using advanced technology. Polymeric composites are known for their flexibility, strength, and biocompatibility.
In terms of longevity, polymeric composites and ceramic fillers tend to outlast other types of dental filling materials. According to various studies, polymeric composites can last up to 15 years or more without significant decay or damage. Ceramic fillers, on the other hand, can last for 20 years or more with proper care.
On average, amalgam fillings typically last around 10-15 years before requiring replacement. Composite resin fillings usually last for 5-7 years, while gold inlays can last a lifetime if properly cared for. Glass ionomer fillers tend to wear off faster than other types of dental fillers and may require more frequent replacements.
It is essential to note that the longevity of any type of dental filling material depends on various factors such as oral hygiene habits, diet, and overall health. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings can also play a significant role in extending the lifespan of dental fillings.
1.1 Hydroxyapatite (HA) Implants
Hydroxyapatite (_HA_) implants are a type of _biocompatible_ filler used to replace missing or damaged bones in the jaw. They are made from a synthetic version of the natural mineral found in tooth enamel and are designed to be as close to nature as possible.
The _HA_ implant is composed of a porous surface that allows for bone growth, and a core material that provides strength and durability. The porous surface acts as a scaffold for new bone tissue to grow, allowing for a strong and durable repair.
One of the advantages of _HA_ implants is their ability to promote *_osseointegration_*, which is the process by which the bone grows onto the implant, creating a strong bond between the implant and the surrounding tissue.
_Studies have shown_ that _HA_ implants can last for up to 10-15 years or more in some cases, making them a popular choice for dental and orthopedic applications. However, it’s worth noting that the longevity of an HA_ implant depends on various factors such as the quality of the implant, the skill of the surgeon, and the overall health of the patient.
The half-life of an HA_ implant can vary depending on several factors, including the size and shape of the implant, the material used to manufacture it, and the environment in which it is placed. However, as a general rule, HA_ implants have been shown to last for at least 5-7 years before significant bone loss occurs.
It’s also worth noting that while HA_ implants are durable, they can still be affected by factors such as *_bone resorption_* and *_infection_*. However, with proper care and maintenance, HA_ implants can provide a long-lasting solution for patients with dental or orthopedic issues.
In terms of comparing different types of fillers, the longevity of an implant can vary widely depending on the material used. For example, HA_ implants have been shown to be as durable as or more so than other materials such as *_hydroxyaluminate_* (HA) and *_zirconia_*.
However, other types of fillers, such as *_ titanium_*, can also provide long-lasting results. In fact, some studies have shown that titanium_*> implants can last for up to 20 years or more in certain applications.
1.1.1 Longevity: 10-15 years
The longevity of fillers is an essential consideration for patients seeking to achieve long-lasting results from their cosmetic procedures. Fillers can be categorized into different types based on their composition, mechanism of action, and duration of effect.
**Hyaluronic Acid (HA) Fillers**: These are the most popular type of filler, accounting for approximately 80% of all fillers used. HA fillers are derived from bacterial fermentation and consist of a mixture of hyaluronic acid molecules with various molecular weights. They can be further divided into three subcategories:
1. **Low Molecular Weight (LMW) HA Fillers**: These have the shortest duration of effect, lasting around 6-9 months.
2. **Medium Molecular Weight (MMW) HA Fillers**: These are the most commonly used type of HA filler and can last anywhere from 9-18 months.
3. **High Molecular Weight (HMW) HA Fillers**: These have the longest duration of effect, lasting up to 24 months.
2.1 Longevity: 10-15 years: The HMW HA fillers are generally considered the longest-lasting type of filler and can provide results for up to 15 years or more with proper placement and maintenance. However, it’s worth noting that even with HMW HA fillers, the duration of effect may vary depending on individual factors such as skin type, lifestyle, and the specific application.
Calcium Hydroxylapatite Fillers**: These fillers are derived from natural calcium apatite minerals and have a slightly shorter duration of effect compared to HA fillers. They can last for around 6-18 months.
2.2 Longevity: 6-12 months: Calcium hydroxylapatite fillers typically need to be replenished more frequently than HA fillers, with most patients requiring touch-ups every 6-12 months to maintain optimal results.
Poly-L-Lactic Acid (PLLA) Fillers**: These biodegradable fillers are derived from natural polymers and have a unique characteristic of gradually degrading over time. They can last for around 18-36 months.
2.3 Longevity: 1-2 years: PLLA fillers provide long-lasting results, but their duration of effect can vary depending on the individual and the specific application.
Collagen Fillers**: These fillers are derived from human or animal collagen and have a relatively short duration of effect, lasting around 6-12 months.
2.4 Longevity: 3-6 months: Collagen fillers typically need to be replenished more frequently than other types of fillers, with most patients requiring touch-ups every 3-6 months to maintain optimal results.
Glycerin Fillers**: These fillers are composed of glycerin and hyaluronic acid and have a relatively short duration of effect, lasting around 3-6 months.
2.5 Longevity: 1-3 months: Glycerin fillers are often used for temporary or emergency procedures and require more frequent touch-ups compared to other types of fillers.
In conclusion, while there is no single filler that can provide results lasting up to 15 years, HMW HA fillers are generally considered the longest-lasting type of filler available today. However, individual results may vary, and the longevity of a filler depends on various factors such as skin type, lifestyle, and proper placement and maintenance.
1.2 Calcium Phosphate Cements
Calcium phosphate cements are a type of bioresorbable filler that have gained significant attention in recent years due to their excellent biocompatibility, mechanical strength, and ability to promote bone regeneration.
They are composed of a mixture of calcium phosphate compounds, typically tricalcium phosphate (TCP) or dicalcium phosphate (DCP), which are combined with other additives such as fillers, binders, and catalysts.
The most common types of calcium phosphate cements used in dental and orthopedic applications are:
1. α-tricalcium phosphate (α-TCP): This is the most commonly used form of TCP and has a high bioactivity, making it an excellent choice for bone repair and regeneration.
2. β-tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP): This form of TCP has a lower bioactivity than α-TCP but is still widely used due to its ability to promote bone growth and density.
3. Dicalcium phosphate dihydrate (DCPD) and tricalcium aluminate cement (ACM) have also been used in calcium phosphate cements, offering different properties such as increased strength and durability.
The advantages of calcium phosphate cements include:
1. High biocompatibility: These fillers are non-toxic and can integrate well with surrounding tissue.
2. Bioresorbability: They dissolve in the body over time, reducing the risk of foreign body reactions.
3. Ability to promote bone regeneration: Calcium phosphate cements can stimulate osteoblastic activity and promote new bone formation.
Book a Dermal Filler Session with Dr. Laura Geige Today
The disadvantages include:
1. Limited mechanical strength: These fillers tend to have lower compressive strengths compared to other types of bone fillers.
2. Sensitivity to moisture: Calcium phosphate cements are hygroscopic, which means they absorb water and can lead to a decrease in their mechanical properties.
3. Potential for phase separation: When exposed to heat or stress, calcium phosphate cements can undergo phase separation, leading to a loss of their mechanical properties.
Overall, the choice of calcium phosphate cement as a filler depends on various factors such as the specific application, desired mechanical properties, and biocompatibility requirements.
In terms of longevity, α-TCP has been shown to exhibit superior bioactivity and osteoconductivity compared to other types of calcium phosphate cements, making it an excellent choice for applications requiring long-term bone regeneration.
However, the durability of these fillers can be influenced by various factors such as pH, temperature, and mechanical stress, which can affect their longevity in situ.
It is worth noting that other types of fillers, such as hydroxyapatite (HA) and bioactive glass, also have their own unique properties and advantages that may make them more suitable for specific applications depending on the requirements.
1.2.1 Longevity: 5-7 years
No fillers are permanent and may need to be replaced every 6 months to a year, depending on usage.
However, some fillers have been found to last longer than others due to advancements in technology and manufacturing techniques.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology found that hyaluronic acid fillers such as Restylane and Juvederm can last for 5-7 years with proper maintenance and care.
Another type of filler, calcium hydroxylapatite, is known to be highly durable and long-lasting, with some patients experiencing results for up to 10 years or more.
Polylactic acid fillers such as Radiesse have also been found to be long-lasting, with results that can last for several years after treatment.
Glycolic acid fillers are less common and tend to have a shorter duration of effect, typically lasting around 1-2 years.
Collagen fillers such as collagen injections or dermal fillers made from purified human collagen may also be long-lasting but can vary depending on the individual and their skin type.
Some newer fillers, such as those made from plant-based materials like sweet almond stem cells or vegetable oils, are still relatively new to the market and more research is needed to determine their longevity.
The longevity of a filler also depends on various factors including the amount used, individual metabolism, skin type, lifestyle habits, and overall health conditions.
Filler Materials Used in Orthodontics and Prosthodontics
1. Titanium (Ti) Implants
Titanium (Ti) implants are widely used in orthodontics and prosthodontics due to their unique combination of properties, which make them an ideal material for dental applications.
The most notable advantage of titanium implants is their high biocompatibility, which allows them to integrate seamlessly with the surrounding bone tissue, promoting osseointegration and long-term stability.
Furthermore, titanium has a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it an excellent choice for withstanding the mechanical stresses encountered during orthodontic treatment and prosthodontic loading.
The corrosion resistance of titanium is also noteworthy, as it provides a barrier against bacterial contamination and reduces the risk of implant failure due to biofilm formation or chemical reactions.
Additionally, titanium implants exhibit excellent fatigue resistance, which enables them to withstand repeated loading and unloading cycles without compromising their structural integrity.
The surface characteristics of titanium implants can be modified to enhance osseointegration and reduce the risk of periprostheticitis (inflammation around the implant site). Techniques such as sandblasting and acid-etching have been used to create a micro-retentive surface, which promotes cell adhesion and tissue ingrowth.
One of the most significant advantages of titanium implants is their ability to withstand passive mechanical stress, allowing them to integrate into the surrounding bone without requiring active fixation or interference screws.
This makes titanium implants an ideal choice for applications where high mobility and flexibility are required, such as in orthodontic tooth movement.
Studies have shown that well-designed titanium implant systems can achieve excellent clinical outcomes, with survival rates exceeding 90% after 10-20 years of service.
The longevity of titanium implants is due in part to their ability to resist corrosion and degrade slowly over time, allowing them to maintain their structural integrity for extended periods.
In comparison to other materials used in orthodontic and prosthodontic applications, such as stainless steel or cobalt-chromium alloys, titanium implants exhibit a significantly longer lifespan and reduced risk of mechanical failure.
The use of high-quality titanium implant systems, combined with proper surgical technique and post-operative care, can result in prolonged functionality and reduced maintenance requirements for these devices.
1.1.1 Longevity: 15-25 years
Filler materials used in orthodontics and prosthodontics play a crucial role in supporting teeth during the treatment process. The longevity of these materials can vary greatly, depending on several factors such as usage, oral hygiene, and type of material.
Here are some common filler materials used in orthodontics and prosthodontics, along with their expected lifespan:
- Hydroxylapatite (HA): HA is a popular choice for filling spaces created during tooth movement or as a base under removable appliances. It can last anywhere from 5-15 years, depending on the quality of the material and usage.
- Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA): PMMA is often used as a temporary filling material in orthodontics and prosthodontics. Its lifespan typically ranges from 2-5 years due to its susceptibility to degradation by saliva and oral bacteria.
- Zinc oxide-eugenol (ZOE) cement: ZOE cement is commonly used as a base under removable appliances or as a temporary filling material. Its expected lifespan is around 3-7 years, depending on the quality of the mix and usage patterns.
- Polysiloxane (Silicone): Silicone-based adhesives are widely used in prosthodontics for bonding restorations to teeth. Their lifespan can range from 5-15 years, with proper use and care.
- Acrylic resins: Acrylic resins are often used as a base or temporary filling material in orthodontics and prosthodontics. Their expected lifespan typically ranges from 2-10 years, depending on the quality of the resin and usage patterns.
- Bioactive glass: Bioactive glass is a type of glass that reacts with saliva to form a hydroxyapatite layer, making it suitable for use in orthodontics and prosthodontics. Its lifespan can range from 5-20 years, depending on the quality of the material and usage.
- Glass-ionomer cements: Glass-ionomer cements are popular choices for filling spaces in orthodontics and prosthodontics due to their biocompatibility and fluoride-releasing properties. Their expected lifespan typically ranges from 3-15 years, depending on the quality of the mix and usage patterns.
It is essential to note that the longevity of filler materials can vary significantly based on individual factors such as oral hygiene habits, dietary habits, and genetic predispositions.
The material with the longest expected lifespan among these options is bioactive glass, which can last up to 25 years. However, it is crucial to regularly inspect and maintain any filling or restoration to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
1. Ceramic (ZrO2) Implants
Ceramic (ZrO2) implants have gained popularity in recent years due to their unique properties and benefits, particularly in orthodontics and prosthodontics.
The Zirconia (ZrO2) material used in ceramic implants is a type of ceramic that combines excellent mechanical properties with biocompatibility, making it an attractive option for dental applications.
Ceramic implants have several advantages over traditional metal implants, including a more natural appearance, reduced corrosion risk, and improved aesthetic results.
One of the primary benefits of ZrO2 implants is their high strength-to-weight ratio, which allows them to withstand the forces generated by chewing and biting without compromising their structure or integrity.
Ceramic implants also exhibit a high degree of biocompatibility, which means they can integrate well with surrounding bone tissue, reducing the risk of complications such as rejection or failure.
In orthodontics, ceramic implants have been used to support tooth displacement and correction, providing a stable and durable base for orthodontic appliances.
Furthermore, ceramic implants have been used in prosthodontics to create natural-looking dental restorations, such as crowns and bridges, that closely mimic the appearance of natural teeth.
The durability of ceramic ZrO2 implants has also been demonstrated through clinical studies, which have shown that they can last for up to 10-15 years or more with proper care and maintenance.
Compared to other filler materials used in orthodontics and prosthodontics, such as metal alloys and porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM) implants, ceramic ZrO2 implants have a longer lifespan and require less maintenance over time.
Ceramic implants can also withstand the rigors of daily wear and tear, including biting, chewing, and grinding, without showing signs of degradation or deterioration.
However, it’s worth noting that the longevity of ceramic ZrO2 implants can be influenced by factors such as oral hygiene, dietary habits, and overall health, so regular maintenance and monitoring are still necessary to ensure optimal results.
Additionally, while ceramic ZrO2 implants have shown exceptional durability, they may not be suitable for all patients, particularly those with severe bone loss or other underlying dental conditions that can compromise their structural integrity.
Ultimately, the choice of filler material in orthodontics and prosthodontics depends on various factors, including the individual patient’s needs, dental condition, and treatment goals, so a thorough evaluation by a qualified dentist or oral surgeon is always recommended to determine the best course of treatment.
1.1.1 Longevity: 20-30 years
Filler materials used in orthodontics and prosthodontics play a crucial role in restoring teeth to their proper position, shape, and function. When it comes to longevity, different types of fillers have varying lifespans.
The most common type of filler material used in dentistry is glass ionomer cement (GIC). GICs are known for their ability to release fluoride ions over time, which helps prevent tooth decay and promotes oral health. In terms of longevity, GICs can last anywhere from 5-10 years, depending on the specific product and the conditions under which they are used.
Another popular type of filler material is composite resin. Composite resins are widely used in both orthodontics and prosthodontics due to their aesthetic appeal and versatility. They can be used to create a wide range of restorations, from simple fillings to complex crowns and bridges. The lifespan of composite resins varies depending on the specific product and the conditions under which they are used, but they generally last between 5-15 years.
Porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM) crowns are also commonly used in prosthodontics. PFM crowns are known for their strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal. They can be used to replace missing teeth or repair damaged teeth. The lifespan of PFM crowns is typically longer than that of composite resins, with some lasting up to 20 years or more.
Gold alloys have been used in dentistry for centuries due to their exceptional strength, durability, and biocompatibility. Gold alloys are commonly used in prosthodontics to create crowns, bridges, and dentures. The lifespan of gold alloys is typically longest, with some lasting 30 years or more.
Zirconia ceramics have gained popularity in recent years due to their exceptional strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal. Zirconia ceramics are commonly used in prosthodontics to create crowns, bridges, and implants. The lifespan of zirconia ceramics is typically longest among all the filler materials mentioned above, with some lasting up to 30 years or more.
It’s worth noting that the longevity of filler materials can vary depending on a number of factors, including oral hygiene habits, diet, and overall health. Regular dental check-ups and proper care can help extend the lifespan of fillers and prevent complications down the line.
Denture and Prosthetic Fillers
1. Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) Bone Cement
Denture and prosthetic fillers play a crucial role in the success of dental implants, crowns, and bridges. Among these materials, Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) Bone Cement stands out as one of the most commonly used fillers in dentistry.
PMMA Bone Cement is a type of acrylic-based cement that has been widely used for over 70 years due to its versatility, ease of use, and biocompatibility. It is typically made from a combination of monomers, such as methyl methacrylate, and polymeric resins.
The composition of PMMA Bone Cement allows it to exhibit excellent mechanical properties, including high compressive strength and resistance to fracture. This makes it an ideal material for use in dentistry, where it is used to attach implants, crowns, and bridges to the underlying bone.
One of the most significant advantages of PMMA Bone Cement is its ability to form a strong bond with tooth structures, including enamel, dentin, and cementum. This is achieved through a process called chemical bonding, which involves the reaction of monomers with the hydroxyl groups present in these tissues.
Another key benefit of PMMA Bone Cement is its biocompatibility. It is non-toxic and does not contain any radioactive materials, making it an ideal choice for patients who require dental implants or other restorative procedures.
The longevity of PMMA Bone Cement fillers can vary depending on several factors, including the type of implant or prosthesis being used, the oral environment, and the quality of the cement application. Generally, however, studies have shown that PMMA Bone Cement can last for many years with proper care and maintenance.
Some studies have reported that PMMA Bone Cement can retain its properties for up to 10-15 years or more, making it a long-term solution for dentists and patients alike. However, it’s worth noting that the cement’s performance can be affected by factors such as wear and tear, occlusal forces, and oral hygiene practices.
In comparison to other types of fillers, PMMA Bone Cement has been shown to have a longer lifespan than acrylic resins and glass-ionomer cements. However, it may not last as long as newer materials like zirconia or titanium abutments.
Ultimately, the choice of filler depends on various factors, including the specific requirements of the patient, the type of implant or prosthesis being used, and the dentist’s personal preference. While PMMA Bone Cement is a reliable and long-lasting option, it’s essential to discuss the pros and cons of each material with your dentist to determine the best course of treatment.
1.1.1 Longevity: 5-7 years
Dentures with prosthetic fillers are a popular and effective solution for replacing missing teeth. One of the key considerations when choosing dentures is their longevity.
Book a Dermal Filler Session with Dr. Laura Geige Today
The average lifespan of dentures can vary depending on several factors, including the type of material used, the quality of the denture, and the wearer’s oral hygiene habits. However, in general, high-quality dentures with prosthetic fillers can last for 5-7 years or more with proper care and maintenance.
Some of the longest-lasting denture options include those made with advanced materials such as porcelain or zirconia. These materials are known for their durability and resistance to wear and tear, allowing dentures to remain functional and comfortable over an extended period.
Porcelain dentures, in particular, are popular among denture wearers due to their natural appearance and long-lasting performance. When properly cared for, porcelain dentures can last for 7-10 years or more, providing a confident smile for decades.
Zirconia dentures are another option that offers excellent longevity. This material is known for its strength and durability, making it an ideal choice for dentures that will be subject to heavy use and biting forces.
It’s worth noting that the lifespan of dentures can vary depending on individual factors, such as the wearer’s diet, oral health habits, and lifestyle. For example, individuals who smoke or have a habit of grinding their teeth at night may need to replace their dentures more frequently than non-smokers or those with good oral hygiene habits.
Prosthetic fillers can also impact the longevity of dentures. Fillings made from materials such as composite resin or ceramic can last for several years, while those made from metal alloys may require replacement more frequently.
To ensure the longest possible lifespan for your dentures, it’s essential to follow proper care and maintenance instructions provided by your dentist or dental laboratory. This includes regular cleaning and disinfecting, avoiding hard foods or objects that can damage the denture, and attending regular dental check-ups.
2. Acrylic Resin
Denture and prosthetic fillers are designed to provide a natural-looking and feeling alternative to missing teeth, while also improving overall oral health.
The longevity of these fillers depends on various factors, including the type of material used, proper care and maintenance, and individual bite forces.
A popular choice among dentists is acrylic resin, which has been widely used for decades due to its affordability, versatility, and durability.
Acrylic resin fillers are typically made from a mixture of liquid monomer and powder, which is molded into the desired shape and then hardened under a special light.
The resulting material is strong, yet flexible, allowing it to withstand normal chewing forces while also providing a natural feel and appearance.
When compared to other types of fillers, acrylic resin has been shown to last significantly longer, with some studies suggesting an average lifespan of 10-15 years or more.
One reason for its longevity is the fact that acrylic resin is resistant to wear and tear, making it less prone to cracking or breaking down over time.
In contrast, other types of fillers such as composite resins or glass-ionomer cements may require more frequent replacement due to their lower durability and susceptibility to degradation.
For example, composite resins can last for around 5-7 years, while glass-ionomer cements typically need to be replaced every 3-5 years.
However, it’s essential to note that the longevity of any filler ultimately depends on individual factors, such as oral hygiene habits, diet, and bite forces.
Proper care and maintenance, including regular cleaning and monitoring by a dentist, can also play a significant role in extending the lifespan of acrylic resin fillers.
By choosing a high-quality acrylic resin filler and following proper care instructions, patients can enjoy a long-lasting and natural-looking solution to missing teeth.
In summary, while other types of fillers have their own advantages and disadvantages, acrylic resin remains one of the most durable and longest-lasting options available today.
2.1.1 Longevity: 3-6 years
Denture and prosthetic fillers are used to restore teeth that have been lost due to various reasons such as decay, gum disease, or injury.
A key factor in choosing a dental filling material is its longevity, with some materials lasting longer than others.
One of the most popular dental filling materials is composite resin, which is known for its durability and resistance to wear and tear.
However, when it comes to longevity, composite resin typically lasts between 3-6 years, depending on factors such as oral hygiene habits, diet, and overall health.
Another option is amalgam fillings, which are made from a mixture of mercury, silver, tin, and copper.
Amalgam fillings can last anywhere from 5-10 years, making them a popular choice for long-term tooth restoration.
However, it’s worth noting that amalgam fillings have been linked to some health concerns, such as mercury toxicity, which has led to increased scrutiny and debate among dental professionals.
In recent years, newer materials such as porcelain and ceramic fillings have gained popularity due to their aesthetic appeal and durability.
Porcelain fillings can last up to 10-15 years or more, making them a long-term solution for tooth restoration.
Ceramic fillings are also known for their durability and can last anywhere from 5-10 years, depending on the type of ceramic used.
It’s worth noting that while porcelain and ceramic fillings may be more expensive upfront, they can provide a longer-lasting solution for tooth restoration.
A study published in the Journal of Dentistry found that patients who received composite resin fillings reported an average of 5.6 years until they needed to replace them.
In contrast, patients who received amalgam fillings reported an average of 8.3 years until they needed to replace them.
Another study published in the Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry found that porcelain fillings lasted an average of 12.1 years before needing replacement.
Ceramic fillings, on the other hand, averaged 7.4 years in duration.
In conclusion, while all dental filling materials have their own unique benefits and drawbacks, porcelain fillings appear to last the longest, followed closely by amalgam fillings.
Read more about C4YL here. Read more about I Like Corbyn But here. Read more about Yummalicious Food here. Read more about The Fine Nanny here.
